
Prosthetics are artificial devices or components designed to replace, enhance, or support missing or impaired body parts, typically limbs. They serve as a crucial and life-changing solution for individuals who have experienced limb loss due to congenital conditions, injury, illness, or amputation. Prosthetic devices are meticulously engineered to replicate the form and function of natural limbs, enabling individuals to regain mobility and improve their quality of life. Here is a more detailed description of prosthetics
Ask The Expert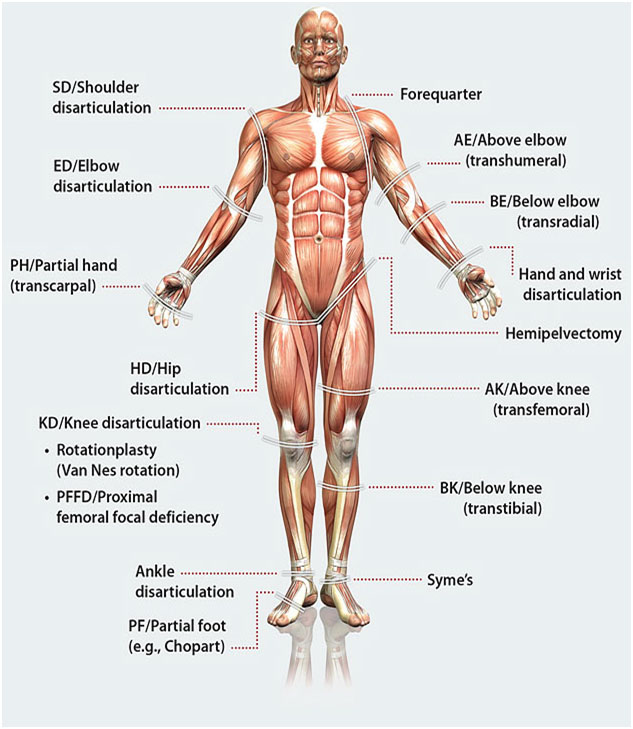
Prosthetics come in various forms, catering to different levels of limb loss and individual needs. Common types include lower extremity prostheses for legs and upper extremity prostheses for arms. They can also be classified based on the level of amputation, such as transtibial (below-the-knee), transfemoral (above-the-knee), transradial (below-the-elbow), or transhumeral (above-the-elbow) prostheses.
A typical prosthetic limb comprises several components, including
The socket is custom-designed to fit over the residual limb comfortably, providing a secure attachment point for the prosthesis.
These are used to cushion and protect the residual limb, enhancing comfort and fit.
A pylon or support structure connects the socket to the terminal device (foot, hand, or specialized attachment).
Some prosthetic limbs have articulating joints to mimic natural movement and improve stability.
Prosthetic components are made from advanced materials, such as lightweight plastics, carbon fiber, and metals. Myoelectric prostheses incorporate electronic components and sensors that allow users to control their artificial limb using muscle signals from the residual limb.
Prosthetic components are made from advanced materials, such as lightweight plastics, carbon fiber, and metals. Myoelectric prostheses incorporate electronic components and sensors that allow users to control their artificial limb using muscle signals from the residual limb.
After receiving a prosthetic limb, individuals typically undergo rehabilitation to learn how to use the device effectively. This process includes gait training, strengthening exercises, and activities to improve dexterity and functionality.
Ongoing research and technological advancements continue to improve prosthetic design and functionality. Innovations include computerized joints, microprocessor-controlled knees and elbows, and 3D printing for customized sockets.
Prosthetics have a profound impact on the lives of those who use them, enabling them to regain independence and engage in a wide range of activities, from everyday tasks to sports and recreation. The field of prosthetics is dedicated to enhancing the quality of life for individuals with limb loss, ensuring that they can lead active and fulfilling lives.